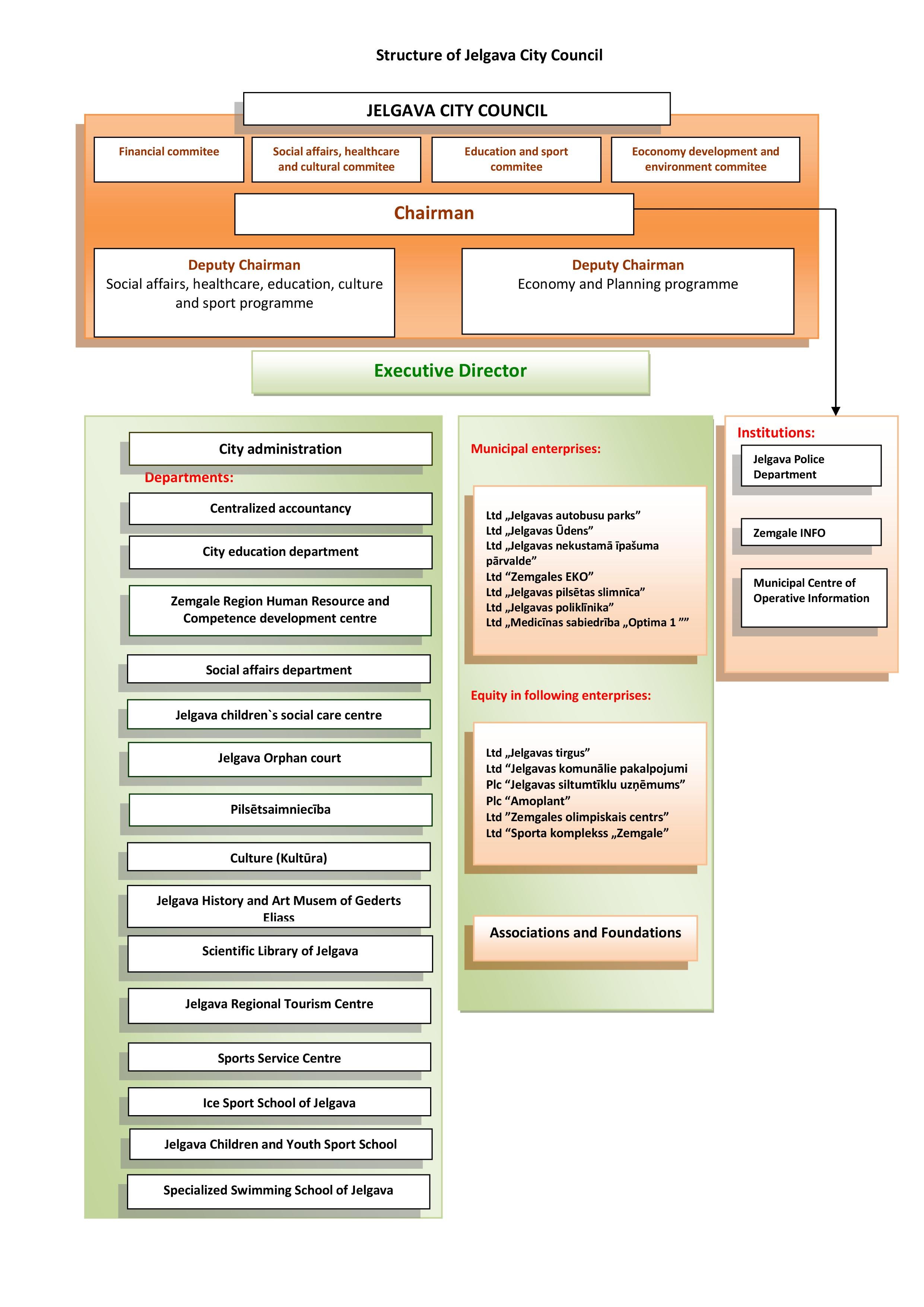
Structure
By law “On local governments” section 15, the autonomous functions of the local government are as follows:
1) to organise for residents the provision of utilities (water supply and sewerage; supply of heat; management of municipal waste; collection, conducting and purification of waste water) irrespective of the ownership of the residential property;
2) to look after the public services and facilities, and the sanitary cleanliness of their administrative territory (building, reconstruction and maintenance of streets, roads and public squares; lighting of streets, public squares and other areas designated for public use; development and maintenance of parks, public squares and green zones; control of collection and removal of waste; flood control measures; establishment and maintenance of cemeteries and places for burial of dead animals);
3) to determine procedures for the utilisation of public-use forests and waters if it is not specified otherwise by law;
4) to provide for the education of residents (ensuring the specified rights of residents to acquire primary and general secondary education; ensuring children of pre-school and school age with places in training and educational institutions; organisational and financial assistance to extracurricular training and educational institutions and education support institutions, and others);
5) to maintain culture and facilitate the preservation of traditional cultural values and the development of creative folk activity (organisational and financial assistance to cultural institutions and events, support for the preservation of cultural monuments, and others);
6) to ensure access to health care, as well as to promote a healthy lifestyle of residents and sport;
7) to ensure social assistance (social care) to residents (social assistance for poor families and socially vulnerable persons, ensuring places for old people in old-age homes, ensuring places for orphans and children without parental care in training and educational institutions, provision of overnight shelters for the homeless, and others);
8) to take care of guardianship, trusteeship, adoption and the protection of the personal and property rights and interests of a child;
9) to provide assistance to residents in resolving issues regarding housing;
10) to facilitate economic activity within the relevant administrative territory, and to be concerned about reducing unemployment;
11) to issue permits and licences for commercial activity, if such is provided for by law;
12) to participate in ensuring public order and to combat drunkenness and immorality;
13) in accordance with the territorial planning of the relevant local government, to determine land utilisation and procedures for its development;
14) to ensure in their relevant administrative territory the lawfulness of the construction process;
15) to perform civil status document registrations;
16) to collect and provide information necessary for State statistics;
17) to perform the necessary measures for elections of city or county councils;
18) to participate in ensuring civil defence measures;
19) to organise public transport services;
20) retracted [17 July 2008];
21) to organise continuing education for teaching staff and pedagogical methodology work;
22) to conduct, in the relevant administrative territory, the registration of children residing therein; and
23) to implement the protection of the rights of the child in the relevant administrative territory.